The antibiotic emergency. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) . The worlds most urgent public health problem.
2/17/2025
David Munday
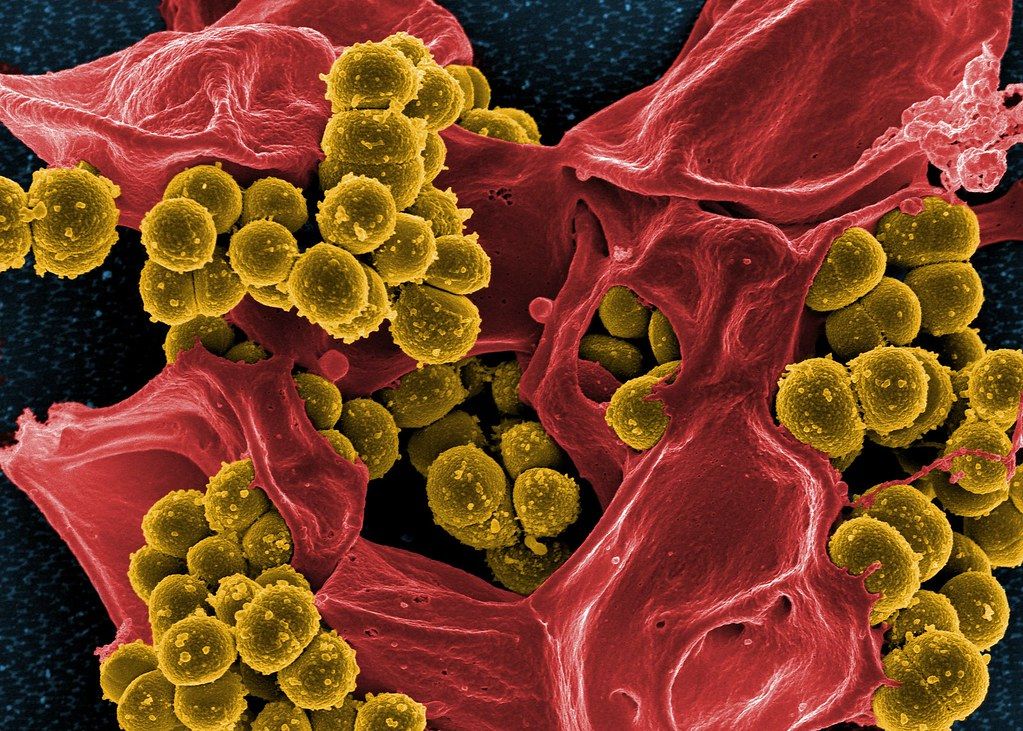
The antibiotic emergency is a global health crisis caused by antimicrobial resistance (AMR). AMR is when bacteria and microbes evolve to survive antibiotics, medicines that generally kill them.
Consequences of AMR: -
Increased risk of infections. AMR makes it harder to treat common infections such as leg ulcers and Caesarian section wounds.
Increased risk of death: - AMR is associated with more deaths, especially in adults over the age of 70. AMR was associated with nearly 5 million deaths in 2019. The figures get worse as time goes by. A 2024 study published in the Lancet estimates that 39 million deaths will occur due to antibiotic resistance between 2025 and 2050. (Equivalent to three deaths every minute). This is a 67.5% increase from 2021.
Increased risk of complications:- AMR increases the risk of complications from routine procedures such as surgery and childbirth. Infections such as peritonitis after a caesarian section can be fatal. The rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci complicates caesarian recovery. Post caesarian peritonitis is associated with a mortality rate of 25% in the main referral hospital in Kigali, Rwanda.
AMR can potentially affect people at any stage of life as well as healthcare, veterinary and agricultural industries.
Economic impact:- AMR has a significant economic impact on developing countries.
The United States Centre for Disease Control considers AMR to be the world’s most urgent public health problem.